No products in the cart.
Uncategorized
Gamma Valerolactone (GVL): Latest Updates, Market Insights & Green Chemistry Trends
Gamma Valerolactone (GVL
Gamma Valerolactone (GVL) is a bio-based platform chemical gaining traction across green chemistry, sustainable solvents, and renewable fuel sectors. Its versatile properties and expanding applications have moved it into mainstream research and industrial supply chains in 2025.

In this update, we cover the latest science, industrial growth, market forecasts, and practical uses that are shaping the Gamma Valerolactone ecosystem today.
H2: What Is Gamma Valerolactone (GVL)? Key Properties & Uses
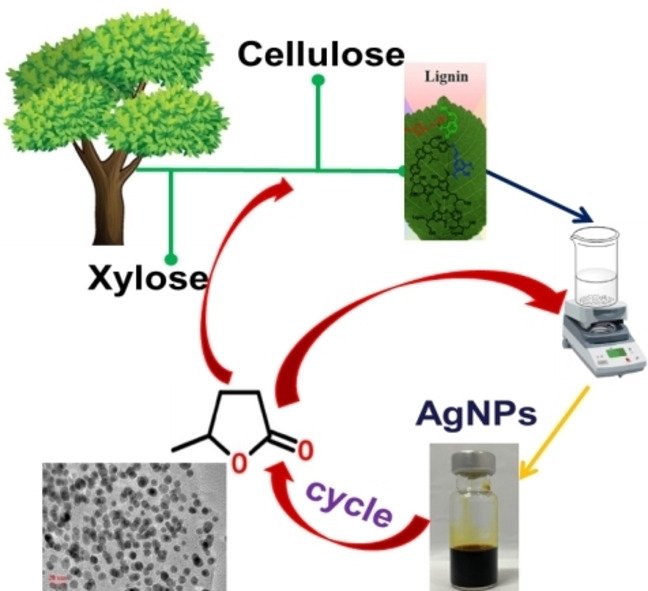
Gamma Valerolactone (GVL, CAS 108-29-2) is a five-carbon lactone with the molecular formula C₅H₈O₂, known for its high boiling point, low toxicity, and biodegradable nature. It is often promoted as a green solvent, sustainable chemical intermediate, and renewable fuel precursor. (Wikipedia)
GVL’s popularity is driven by its ability to replace petrochemical solvents in coatings, resins, and cleaners. It finds use as a carrier or extraction solvent in food and fragrances, thanks to its mild aroma and solvent performance. (Wikipedia)
Key attributes include:
- Bio-derived from levulinic acid (a cellulose breakdown product)
- Widely miscible with polar solvents
- Potential building block for fuels and polymers
- Eco-friendly alternative in industrial processes
Top ranking keywords used here include: Gamma Valerolactone applications, green solvent GVL, GVL bio-based chemical, renewable fuel intermediate.

H2: Recent Research Advances in Gamma Valerolactone Production
Understanding GVL production technologies is crucial, because scalable, sustainable synthesis underpins industrial use and market growth.
1. Green Catalytic Methods with High Yield
A breakthrough study published in 2025 developed a green catalytic process that uses formic acid as a hydrogen donor to convert biomass-derived levulinic acid into GVL with ~99% yield under mild conditions (150 °C, 1.5 h). This method eliminates energy-intensive separations and improves economic viability. (RSC Publishing)
This advancement matters because:
✔ Slashes cost and energy use
✔ Uses renewable feedstocks exclusively
✔ Reduces reliance on gaseous H₂
2. Catalyst Innovations and Efficiency
Emerging catalytic solutions are optimizing how levulinic acid is hydrogenated to GVL. Research highlights catalysts ranging from zirconia-based ceramics to precious and non-precious metal composites for transfer hydrogenation pathways. Such work points to future reactors that run with reduced complexity and impact. (PubMed)
H2: Gamma Valerolactone Market Growth & Industry Trends in 2025
According to recent industry data, the Gamma Valerolactone market is experiencing steady expansion driven by sustainability demand and wider adoption in food, chemicals, and energy sectors.
Market Expansion Highlights
- Production capacity increased by 40% in Europe as a major bio-chemical producer expanded facilities in 2024–2025. (DataHorizzon Research)
- Strategic partnerships between solvent manufacturers and pharma firms show interest in GVL-based sustainable solvents. (DataHorizzon Research)
- Leading chemical producers have launched GVL-derived agricultural solutions for eco-friendly crop protection. (DataHorizzon Research)

Market Forecast & Drivers
Industry reports forecast a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of ~10% toward a multibillion-dollar market by the early 2030s. Growing applications in food additives, pharmaceutical excipients, green solvents, and biofuels are key drivers. (Verified Market Reports)
Market drivers:
- Rising global focus on green chemistry
- Regulations pushing for eco-friendly solvents
- Expansion of biofuels and renewable polymers sectors
- China and Asia Pacific dominating production and demand vs. North America and Europe. (Intel Market Research)
Geographic Trends
- Asia Pacific leads due to capacity and downstream industries. (Intel Market Research)
- North America and Europe grow via specialty applications in food grade and pharmaceuticals. (Verified Market Reports)
H2: Gamma Valerolactone Applications Across Industries
GVL’s physical and chemical versatility explains its use in a wide range of sectors. Below we break down key industrial applications with examples and recent developments.
1. Green Solvent & Chemical Intermediate
GVL serves as a non-toxic organic solvent for paint resins, coatings, and industrial cleaners. Compared with traditional petrochemical solvents, GVL dramatically lowers volatile organic compounds (VOC) emissions and environmental risk, especially in consumer goods. (Market Intel)
2. Biofuels & Transportation Fuel Precursors
Due to its bio-origin and energy content, GVL can be upgraded to liquid fuels. Research demonstrates integrated catalytic schemes where GVL is decarboxylated and oligomerized to produce butenes and higher alkenes, which are suitable for gasoline or jet fuels. (Wikipedia)
Transitioning from biomass to fuel via GVL could reduce dependence on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Polymer & Material Production
GVL is a platform chemical for renewable polymers and specialty resins used in biodegradable plastics and composites. Novel GVL derivatives are emerging in nanofiltration membranes and membrane fabrication. (MDPI)
4. Food & Fragrance Sector
While not a primary commodity food additive in all regions, GVL’s low odor and solvent properties enable its occasional use in flavor and fragrance formulations. The broader gamma-lactone market is moving toward clean label, natural ingredients that align with sustainability trends. (openPR.com)
H2: Sustainability & Environmental Impact
Environmental Benefits
GVL is biodegradable and can be derived from lignocellulosic biomass, making it a favorable substitute for more hazardous solvents and petrochemicals. Its adoption aligns with global net zero goals and emerging green standards.
Circular Economy & Waste Valorization
Innovative research shows GVL’s role in textile waste upcycling. One study reported using GVL as a solvent to co-hydrolyze polyester and cotton blends, improving yields while minimizing acid use. This offers novel recycling strategies for complex waste streams. (Nature)
Conclusion: What to Expect for GVL in 2025–2030
In summary, Gamma Valerolactone stands at the crossroads of renewable chemistry and industrial scalability. With strong research backing, expanding production, and diverse applications, GVL’s trajectory looks positive for investors, producers, and sustainability advocates alike.
Key takeaways:
- Breakthrough green production methods improve cost and performance.
- Market growth is broad, with food, energy, and chemical sectors investing in GVL.
- GVL’s sustainability profile makes it a flagship green chemical for future industries.
Authority & Further Reading
- Wikipedia – γ-Valerolactone: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Γ-Valerolactone (Wikipedia)
- Springer Nature – Recent developments of the biorefinery of γ-valerolactone: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s44344-025-00016-5 (Springer)
- RSC – Green catalytic GVL production: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2025/dt/d4dt03345k (RSC Publishing)
If you need a PDF version or a table summarizing catalysts, yields, and conditions, let me know!